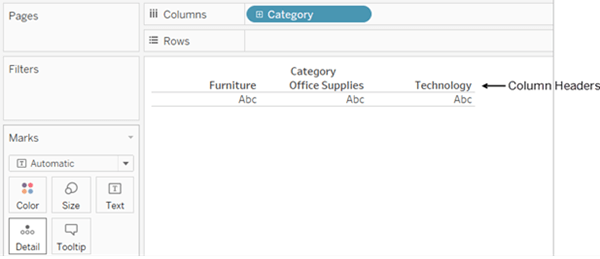
Discrete fields
- Discrete in general means “individually separate and distinct”.
- In Tableau Discrete fields are Blue in colour.
- Generally, discrete fields are considered finite in range.
- They usually add headers to the view.
- The Data in Tableau can be categorised into ‘Dimensions and Measures’.
- Dimensions contain qualitative values such as names, dates, age, product Id etc.
- Dimension gives the user a categorical data.
- Dimensions can be put into filter shelf, once put it asks the user to select between the categories.
- Dimensions affect the level of details in the view. The user can see it by looking to the marks given on the left side of the view when the user adds a dimension the number of marks increases.
- Discrete Dimensions are more common and Discrete Measures are less common in Tableau.
- Date values can be both Discrete and Continuous.
- When the Discrete fields are dropped on the color mark card, Tableau displays a categorical palette and automatically assigns a color to each value of the field.
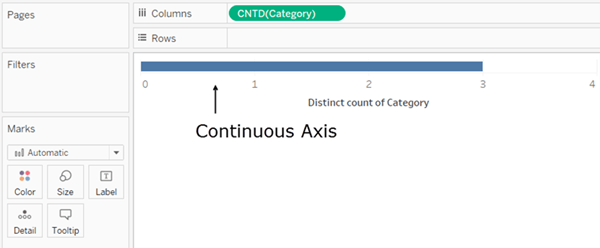
Continuous fields
- Continuous in general means “series or unbroken chain without interruption”.
- In Tableau Continuous fields is Green in colour.
- Continuous fields are mostly considered as infinite in range.
- They add axes to the view.
- Measures in Tableau are quantitative values i.e. the values that can be measured such as sales value, profit/loss values etc.
- Measures add aggregation to the view. When the user drags a measure to the view, Tableau applies an aggregation to the measure (by default).
- Measures can also be put into the filter shelf. When the user drops a continuous measure into the filter shelf, Tableau firstly prompts to choose an aggregation for the filter and then prompts to specify how to filter the continuous range of values.
- When the user drops a continuous dimension into the filter shelf, Tableau just prompts to specify how to filter the continuous range of values.
- Continuous measures are more common and continuous dimensions are less common.
- Date values can be both continuous and discrete.
- When continuous fields are dropped on color in the marks card, Tableau displays a Diverging palette with a continuous range of colours.
Try answering these Tableau multiple-choice questions quiz and exams to test your skills in the Tableau.
- Tableau Desktop Specialist Practice Questions for Global Certification (Practice quiz)
- Tableau Desktop Specialist (Practice Exams)
If you have any questions, shoot us an email at info@datavizguru.com.